Cervical Disc
NECK PAIN RELATING TO HERNIATED DISC, PROLAPSED DISC, SLIPPED DISC Slipped disc, bulging disc, prolapsed disc… these are all common terms used to define types of injury to the discs which sit between the vertebrae bodies (bones) of the spine. Commonly described as the “cushions” or “shock absorbers” of the spine, these circular pads of cartilage are composed… Read more »
Nerve Compression
NERVE COMPRESSION / IRRITATION IN THE NECK As the pairs of nerve roots leave the cervical spine (neck), they can become subjected to injury either as a result of physically restriction or chemically irritation. In the vast majority of cases, this is due to a prolapsed disc and sometimes bony growths from degenerative joints, known as osteophytes,… Read more »
Whiplash Associated Disorders
WHIPLASH ASSOCIATED DISORDERS Injuries to the neck caused by a sudden movement of the head backwards and forwards or sideways are referred to as “whiplash”. This is commonly associated with road traffic accidents, especially rear impact collisions [1,2], but can also occur in sporting injuries such as rugby and boxing. So what exactly happens to… Read more »
Intercostal Muscle Strain: What It Is, Symptoms & Treatments
Intercostal Muscle Strain: What is it? The thoracic spine consists of twelve vertebrae which each connect to a pair of ribs. The upper seven ribs are connected directly to the chest bone/sternum and are termed true ribs, whereas the lower five ribs do not attach directly to the sternum and are defined as false ribs…. Read more »
Compression Fracture
COMPRESSION FRACTURES Compression fractures are common fractures found in both the thoracic and lumbar spine and result from trauma involving a combination of compression and flexion. In the elderly, osteoporosis is a frequent contributing factor to the development of these wedge-shaped fractures – and these so called “grandma fractures” can also occur spontaneously during everyday… Read more »
Upper Cross Syndrome
UPPER CROSS SYNDROME Upper Cross Syndrome describes a characteristic pattern of muscle imbalances which frequently relates to some office-based sitting postures. As a consequence of these imbalances, patients may actually describe a range of symptoms such as mid back aching and stiffness, neck pain and restricted range of motion and headaches. The characteristic pattern of… Read more »
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)
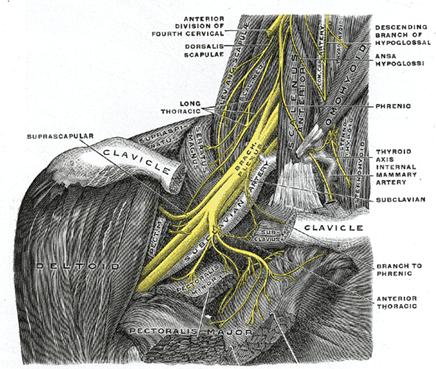
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (TOS) Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of conditions characterised by compression or irritation of the brachial plexus and blood vessels (subclavian artery and vein) as they travel from the neck into the upper limb. The passage of this neurovascular bundle can be compromised by any soft tissue or bony enlargement which… Read more »
Thoracic Disc Prolapse/Herniation
MID BACK PAIN RELATING TO HERNIATED, PROLAPSED, SLIPPED DISC The thoracic spine is located between the cervical spine (neck) and the lumbar spine (low back). It consists of 12 separate vertebrae which are named from the top to the bottom as T1 to T12. The mobility in this region is restricted because of the presence… Read more »
Scoliosis
SCOLIOSIS When looking at the adult spine from the side, it is apparent that the spine is not straight. Instead, the spine depicts a gentle “S-shaped curve” with the low back and the neck having a gentle inward (concave) curve whilst the mid back curvature is the opposite and exhibits an outward (convex) curve. When… Read more »
Thoracic Facet Sprain
THORACIC FACET SPRAIN The thoracic spine, also known as the mid back, is located between the cervical spine (neck) and the lumbar spine (low back). It consists of 12 separate vertebrae which are named from the top to the bottom as T1 to T12. The mobility in this region is restricted because of the presence… Read more »
Cervical Facet Sprain
CERVICAL FACET SPRAIN The cervical spine (neck) consists of seven separate vertebrae which are named from the top to the bottom as C1 to C7. Two facet or zygapophyseal joints are located at the back of each vertebra and are the bony links between the vertebra above and below by means of a superior articular… Read more »
