Wrist/Finger Extensor Strain
WRIST/FINGER EXTENSOR STRAIN OR RSI Overuse injuries of the wrist and forearm not only subject the tendons of the forearm to overload, but can also result in repetitive strain to the muscles which are responsible for extending the wrist and fingers. This type of injury is often grouped together with other diagnoses, such as carpal tunnel… Read more »
Tennis Elbow/Lateral Epicondylitis
TENNIS ELBOW/LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS The medical name for tennis elbow is lateral epicondylitis, as this condition occurs where the tendons of the forearm insert onto the lateral epicondyle of the elbow joint. The lateral epicondyle is the site at which the muscles which bend the wrist and fingers backwards originate. There are many muscles which… Read more »
Elbow Fracture
ELBOW FRACTURE Trauma to the elbow may occur from several different mechanisms, such as falling onto an outstretched hand, falling onto the point of the elbow or receiving a large force directly to the elbow. If you have experienced a history of trauma and show any of the signs or symptoms below, it would be… Read more »
Osteoarthritis (OA) of the Shoulder
OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA) OF THE SHOULDER In the absence of previous trauma, osteoarthritis in the shoulder predominantly occurs in the acromioclavicular joint rather than the glenohumeral joint. Similar to any other joint in the body, osteoarthritis in the acromioclavicular joint occurs secondary to either overuse of the joint or as a consequence of previous trauma, such… Read more »
Biceps Rupture
BICEPS RUPTURE The biceps brachii muscle can rupture either as a consequence of direct trauma or secondary to overuse. Often in the case of overuse, the tendon involved may already exhibit characteristics of a tendinopathy/tendinosis. To complicate matters further, this already weakened tendon may not necessarily be symptomatic prior to the development of a tear. In this… Read more »
Dislocated Shoulder (Glenohumeral Joint)
DISLOCATED SHOULDER (GLENOHUMERAL JOINT) The glenohumeral (GH) joint is the largest and most obvious joint in the shoulder complex. It is described as a “ball-and-socket” joint and consists of an articulation between the glenoid fossa of shoulder blade (which forms the socket) and the head of the humerus (which forms the ball). One of… Read more »
Glenoid Labrum Tear
GLENOID LABRUM TEAR The glenohumeral (GH) joint is the largest and most obvious joint in the shoulder complex. It is described as a “ball-and-socket” joint and consists of an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the shoulder blade (which forms the socket) and the head of the humerus (which forms the ball). One of the… Read more »
Acromioclavicular (AC) Sprain / Separation
ACROMIOCLAVICULAR (AC) SPRAIN / SEPARATION The acromioclavicular joint (AC) is found on the top of the shoulder and is located between the collar bone and part of the shoulder blade defined as the acromion. Through this articulation, the collar bone can act as a strut, maintaining the upper limb away from the thoracic cage… Read more »
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
ADHESIVE CAPSULITIS (FROZEN SHOULDER) Frozen shoulder is medically termed Adhesive Capsulitis and is a condition which affects the capsule around the glenohumeral joint, whereby the capsule becomes inflamed, swollen and contracted. As a consequence, the normal elasticity of the capsule is replaced by pain and stiffness. https://media.physitrack.com/educational_videos/efc907ee-35e2-425c-86aa-a83e468a9676/video_720p.mp4 The cause of adhesive capsulitis is largely unknown. This… Read more »
Subacromial Bursitis
SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The subacromial bursa is a fluid filled sac, which is located under the acromion, and functions to decrease friction between the rotator cuff and coracoacromial arch. Bursae are found in many locations within the body such as the knee and hip and like any soft tissue, can become injured. In the case… Read more »
Rotator Cuff Tears
ROTATOR CUFF TEARS Rotator cuff tears can occur as a consequence of either direct trauma or secondary to overuse. Often in the case of overuse, the tendon involved may already exhibit characteristics of a tendinopathy/tendinosis. To complicate matters further, this already weakened tendon may not necessarily be symptomatic prior to the development of a tear…. Read more »
Bicipital Tendinopathy
BICEPS TENDINOPATHY The biceps brachii muscle is located in the upper arm and is composed of a long and a short head. The long head crosses both the shoulder joint (see below) and the elbow joint, whereas the smaller short head crosses only the elbow joint. The long head originates on the supraglenoid tubercle of… Read more »
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
ROTATOR CUFF TENDINOPATHY To understand the injuries that can occur to tendons of the shoulder, a brief understanding of normal tendon structure is required. A tendon is a tough band off fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone. In response to physical training, the metabolism in tendons changes and, as such, the tendon will adapt… Read more »
Impingement Syndrome
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME The rotator cuff muscles are susceptible to cumulative/overuse injury. One of the leading causes of cumulative injury is poor posture and muscular imbalances, which disrupt the normal biomechanics of the shoulder, leading to alteration in the position of the humerus within the shoulder blade during arm movements. The main rotator cuff muscle,… Read more »
Sacroiliac (SI) Joint Sprain
SACROILIAC SPRAIN There are two sacroiliac (SI) joints located at the back of the pelvis. These strong, stable synovial joints are formed between the sacrum and the ilium of the pelvis. The SI joints are covered by two different kinds of cartilage: the sacral surface has thick hyaline cartilage, and the ilial surface has thinner… Read more »
Piriformis Syndrome
PIRIFORMIS SYNDROME The piriformis muscle is located in the gluteal/buttock region at the back of the pelvis. Anatomically, this muscle originates from the front of the sacrum and inserts onto the hip. Its main actions are to rotate the hip outwards (laterally) when the hip is bent to less than ninety degrees and to rotate… Read more »
Herniated/Slipped Disc Explained: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Slipped disc, bulging disc, prolapsed disc… these are all common terms used to define types of injury to the discs which sit between the vertebrae bodies (bones) of the spine. Commonly described as the “cushions” or “shock absorbers” of the spine, these circular pads of cartilage are composed of tough, fibrous tissue on the outside (annulus fibrosis) and a… Read more »
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)
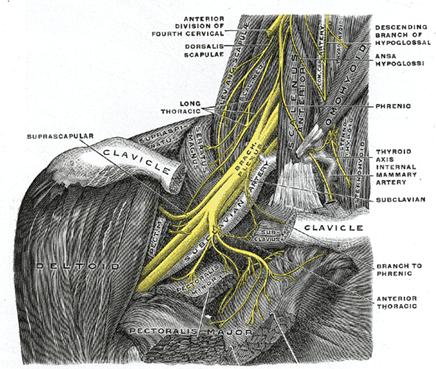
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (TOS) Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of conditions characterised by compression or irritation of the brachial plexus and blood vessels (subclavian artery and vein) as they travel from the neck into the upper limb. The passage of this neurovascular bundle can be compromised by any soft tissue or bony enlargement which… Read more »
